User interface
The SAP C4C solution is characterized by a different approach to the usefulness and ergonomics of work. In contrast to SAP CRM, we have a number of buttons and tabs to our disposal, located on both sides of the screen on side panels, which are shortcuts to applications. Thanks to them, we will effectively check the content of internal announcements, add a new customer or product, plan a meeting or phone call, outline a task, and open up the calendar. We can quickly view the list of employees and products, and further, using the drag-and-drop method, we can add chosen objects to documents, e.g. products to sales opportunities or offers.
SAP Cloud for Customer – personalized user interface
A News feature is available, which works based on an internal communicator. By using the “@" and “*" characters accordingly, we can recall a product or send a message to a chosen employee. This way, we are create active links that take us into the view of a designated person or product.
The SAP CRM interface (so called WebUI) is based on HTML (with a large amount of ABAP), giving configuration and personalization abilities, which are in essence similar to C4C. However, it is characterized by a different concept of ergonomics.
The C4C user interface is a newer generation interface (based on HTML5), more functional for the user, well thought out, using the experiences of the modern B2C application. With a set of high-speed functions handy.
SAP CRM, in spite of possessing similar functions, it sometimes makes difficult to them difficult (e.g., the necessity to scroll the screen or switch between tabs to access them). Admittedly, for some time now we can install dedicated Fiori applications in SAP CRM (e.g. list of customers, sales opportunities, meetings, sales portfolio), which makes work with this tool more pleasant, but this option is not available for the entirety of the SAP CRM functionality, but only for chosen areas.
Client card (a 360 view)
SAP C4C proposes a segmented client card, dividing it into three sections:
- Main data – with information about basic customer data such as addresses, roles, persons responsible, revenue generated or the active level of the sales portfolio;
- Tabs – situated at the top of the screen, they direct us to all business objects, from orders related to the customer, sales data and regions by sales opportunity, offers, activities, visits, relations, product lists, attachments and news;
- The work screen presents the overview of the content of the above tabs, and a nested InsideView application (presenting below the customer’s data from outside of the system, accumulated in an external WWW service, which is an essential added value to C4C).
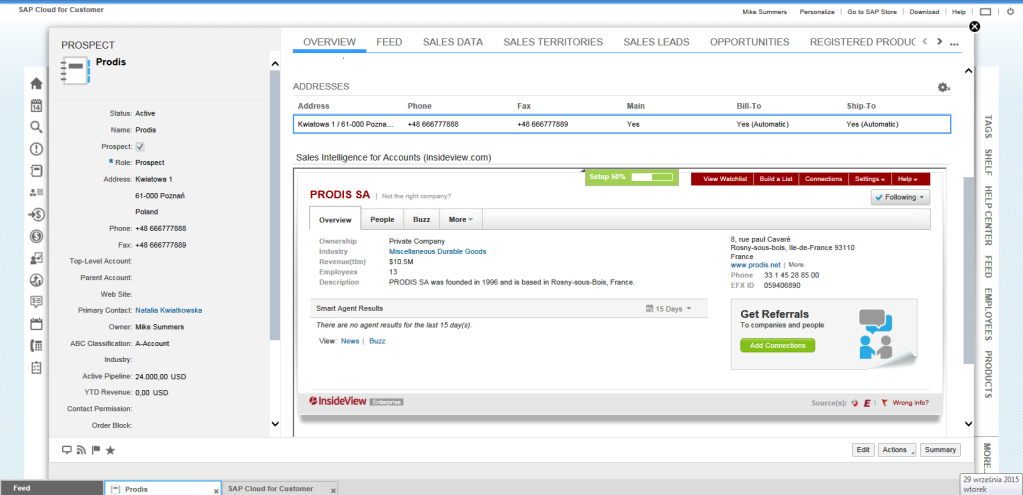
Client Card in SAP Cloud for Customer
In SAP CRM, the available customer card has a default layout, presenting basic customer data on the top (name, address), and below in blocks, e.g. all data can be viewed in tabs without the need to scroll down.
Even though both applications present customer data in a very similar way, working with them in C4C seems more effective.
Trade operations
Functionalities for trade operation management are essentially identical in both of applications. C4C stands out only with the support of a route view through an integrated map in the route-planning field, presenting customer location and making it easier to plan previously created actions. There is a possibility to use e.g. Google or Bing maps.
In C4C, there is also a functionality for mass sending of e-mails to a pre-created target group (it is not a marketing campaign).
In terms of support for Retail Execution processes (fieldwork, control of sales sites), C4C as well as CRM have additional applications with a similar range of functions (for launch e.g. on tablets). They support route realization, with survey form completion for a chosen point of sale, attachment of an image from the store, order entry or repair notification. The Retail Execution 3.0 application for SAP CRM seems more mature, but the application for C4C will soon close in this gap.
Determining prices
The mechanism for the determination of prices is set in the C4C system and is predefined and unmodifiable. It relates to all business processes. It comprises of typical elements such as a price list (for products specific-to-the-customer or a distribution channel), discounts, additional fees, freight costs. A manual entry of the discount amount in the offer is possible. There is also the possibility to directly and automatically ask SAP ERP about the price based on the sale opportunity. In such a situation, we use the pricing procedure located in the SAP ERP sales module.
On the other hand, in SAP CRM, we have basically an identical mechanism for price determination as in SAP ERP. A very complex mechanism, allowing to create price determination procedures containing optional and even complex conditions. Additionally, these procedures can differ for different sale processes – for example, we can determine sale prices differently in the sale of articles or services. We can also use different price determination processes depending on the organizational unit that is realizing the sale or the sales area.
So, in SAP C4C, price determination is simplified and will fulfil basic needs. In organizations that require complex price determination based on a key as well as in multi-department companies, SAP CRM will function better.
The planning and sales forecast
In C4C, there is a function for creating sale forecasts in terms of volume. Through the system, traders can send those forecasts for the approval of department managers. Such a forecast can be used by both a sales specialist and manager to compare sales operations from the same period. From this level, automatically filtered sales opportunities can be viewed. This is an additional tool for sales portfolio reporting, which helps to verify trade actions.
SAP Cloud for Customer – creating the sales forecast
SAP Cloud for Customer contains a sales planning function in time frames – e.g. for a product, product category or the customer. We can enter a sales target in the form of an amount. It is possible to share plans (e.g. between managers and sales specialists), which promotes effective work, while ensuring that data will be stored on the system and not in Excel files exchanged via e-mail.
In SAP CRM, we only have a place in sales opportunities to our disposal (similar to C4C) for forecast entry for a single opportunity (so-called – estimated sale value), and targets for sales specialists in portfolio reporting. Here, we can see the superiority of C4C.
Workflow
Workflow rules configuration in C4C consist of choosing a business object and specifying the condition (equal, different from, etc.; e.g. a status different from a closed one), and then choosing the activity, which is to be automatically executed (field update, e-mail, notification, announcement). Triggering the rule to the recipient can be scheduled for a given moment of time or be executed during the creation, or each save of the object.
In SAP CRM, a whole developer environment is available, which allows configuring and programming workflow mechanisms. Booting-up workflow can be attached in basically any place of the business or technical process in SAP CRM. This provides a broad range of possibilities for additional support of the process beyond the SAP standard. The advantage of SAP CRM in this area is obvious.
Data migration
C4C provides for easy migration of data. Using a tool, we can migrate objects such as:
- employee,
- customer,
- all operations,
- service notifications,
- registered products,
- sale opportunities and offers,
- social media accounts,
- materials,
- product and discount lists,
- price lists.
C4C cares for the transfer of all data constituting the migrated object (statuses, attachments, persons responsible and partners, descriptions, addresses, dates of validity, etc.). After data readout from the file (right before the migration), we are able to directly edit it, which is not possible in the twin SAP CRM tool.
In SAP CRM, on the other hand, we have the external lists mechanism (ELM), with which we can prepare a form for data import with data mappings and then load the data from the file.
We can only import the following data using this mechanism:
- business partners,
- operations (e.g. meetings),
- potential opportunities,
- potential customers.
In addition, there are LSMW mechanisms, which give the possibility of migration for a broader range of objects, but mostly require the programming of the whole mechanism (similar to dedicated ABAP programs). Thus, business users cannot use them.
When comparing the two systems, it should be stated that, in the scope of the above-mentioned objects, migration to C4C seems more effective. However, if there is a need to go beyond this scope, then the flexibility of SAP CRM is its advantage.
Reporting
Apart from the several ready-to-use reports available in C4C, you can use a self-design report tool. By compiling data, filters, types of charts, time ranges, the choice of parameters, we obtain a unique report, which can be seen as a tile on the main screen after saving (so-called – Customer Insight).
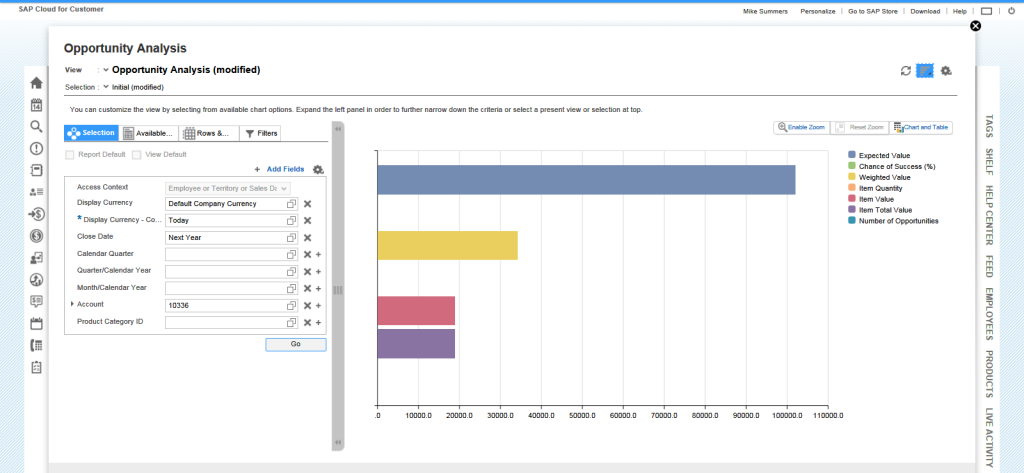
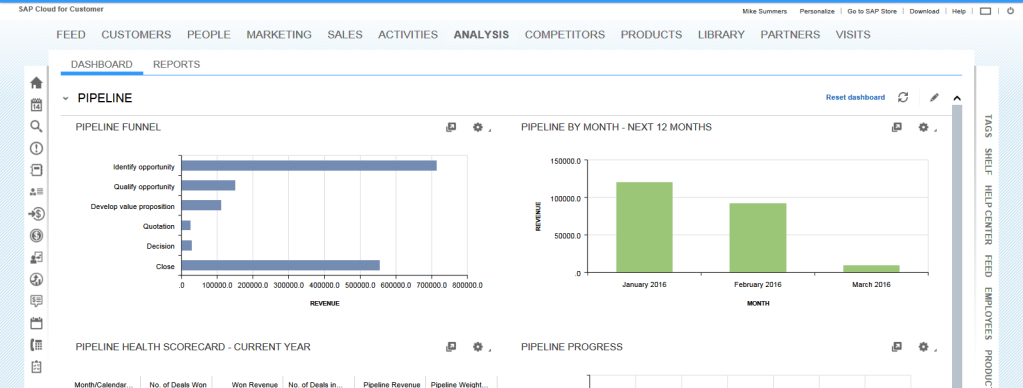
SAP C4C reporting abilities
In SAP CRM, apart from the possibility to report from data storage, we also have standard project portfolio management reports (so-called – PPM) as well as interactive reports (so-called – IR). Sales portfolio reports present data from processed sale opportunities and are a rather closed solution in terms of their development. Interactive reports, on the other hand, provide the possibility to perform a personal report based on the available data (e.g. operations, campaigns, complaints, opportunities). However, they do not give honest data and the possibility to select or to create additional indicators. Generally, they can only be used in simple activities for choosing a basic data set.
These SAM CRM limitations, as well as the wealth of completed operational reports in C4C, make the C4C tool more effective in the perspective of the user and implementation costs.
Implementation time
In general, C4C is a system that is a lot simpler in configuration. Deploying a ready process in this system takes less time than in SAP CRM, even in comparison to the option of SAP CRM implementation in the Rapid Deployment Solution mode (but we can only compare the implementation process in C4C, and which will also be available in CRM). The boot-up time is significantly influenced by the fact that there is no need to buy hardware or a hosting service because the SAP Company offers C4C in the cloud model (SaaS – Software as a Service).
For who?
The answer to the question of which system to choose is difficult because it is impossible to unequivocally identify a typical company – an owner of SAP C4C or SAP CRM. We can imagine both of the applications in a large and a small organization (in terms of turnover, customer numbers, number of sales processes i.e. quotations, as well as the amount of product/services).
A good indicator will be the complexity and sophistication level of the process being sold or serviced. The more detailed and multi-variant it is, the closer we get to SAP CRM (e.g. a large number of supported market segments with the need for diversification of actions or a process that is highly structured, automated, or leads the sales specialist by the hand). On the other hand, if we are ready for more process simplifications (which will definitely affect the application’s time and price!), or– in other words – the more our process is similar to the one offered by C4C – the closer we are to this solution.
Of course, SAP CRM is equipped with a large amount of ready functionalities than C4C (examples include: loyalty management, advanced routing of documents and e-mails, a dynamic ACE rights assignment, managing trade discounts, billing, returns, or specialized additions like integration with RE-FX).
The deciding factor can also be the preferred model of application maintenance in a company, so there is a dilemma: cloud or on-premise. It is of course a large simplification because both of the applications are available in several maintenance model variants.
Summary
SAP Cloud for Customer should be treated as a complete solution that pays special attention to specific business need/process. This tool proposes its own idea for conducting such a process. The decision is up to us if we see it as something valuable. If so, then it is an ideal solution for our company. If not, we are always left with SAP CRM.

Piotr Bieliński, Business Development Manager in the area of CRM-SD, All for One Poland
First of all – identify the needs
The choice of IT tools that support relations with customers is not an easy task because SAP alone has several solutions, which can support CRM processes. Therefore, it is better to focus on the identification of individual needs and the expectations of the company in this area and make such an analysis a starting point. When reviewing your processes that require system support, as well as during the choice tools, it is worth using the support of an experienced partner.
For years, BCC (now All for One Poland) has been implementing and developing solutions that support sales and customer relation management. We were pioneers on the Polish market, leading the first major SAP CRM implementation. We have also developed a proprietary system of extensions responding to specific needs of customers in terms of support for commercial activities. We realize classic SAP CRM implementation projects, which satisfies even the most advanced needs in the area of relations with customers. BCC offer also includes the SPRINT CAM solution, which is a ready-to-use, complete CRM package, based on SAP CRM.
The new solution – SAP Cloud for Customer – completes our advanced offer of CRM solutions for those companies, which are ready to use applications that are available in the cloud.
We also offer a SAP ERP functionality development in the sales and distribution module in accordance with individual needs of our customers. Most of all, based on these experiences, our next proposal was created: the unique CaRuM application that supports daily work of sales specialists using data on customers from the SAP ERP system. CaRuM allows companies working with SAP to improve CRM functions without the need for costly investments in the complex CRM system.
Thanks to the extensive experience encompassing different tools from the SAP offer, we are a proven partner both in the process of needs analysis in the area of customer relations with customers and optimal selection of tools, as well as their implementation and further development.
Piotr Bieliński, Business Development Manager in the area of CRM-SD, All for One Poland
