SAP Landscape Management 3.0 (LaMa) is an advanced tool that enables automation and standardization of SAP system landscape management. The solution provides a unified view of the performance of applications and the entire architecture, ensuring transparency. The flexibility of the system allows for the creation of custom extensions to precisely tailor it to unique business needs.
The solution is available in two versions, which provide ready-made solutions for SAP systems – Standard and Enterprise. The Standard version is available as part of a license for another SAP system, while the Enterprise version is an additional paid extension.
The Enterprise version offers, among other features:
- Creating system copies and carrying out PCA (Post Copy Automation) tasks
- Operations of stopping, starting, and restarting SAP environments
- Managing SAP HANA, including in High Availability solutions
- Implementing SAP notes
- Updating SAP kernels
- Updating ST-API/ST-PI components.
The main features available in the Standard version include the ability to start and shut down SAP environments, including HANA, but without support for High Availability (HA).
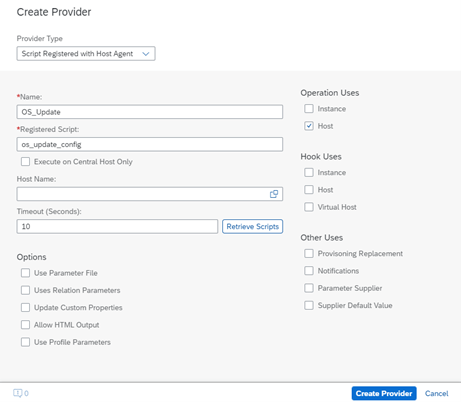
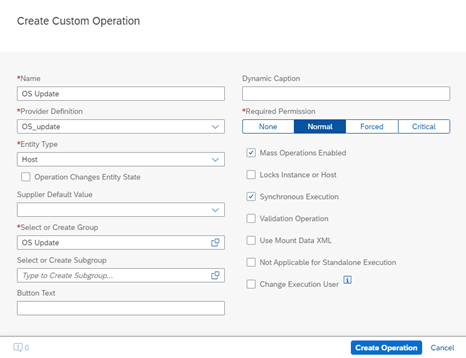
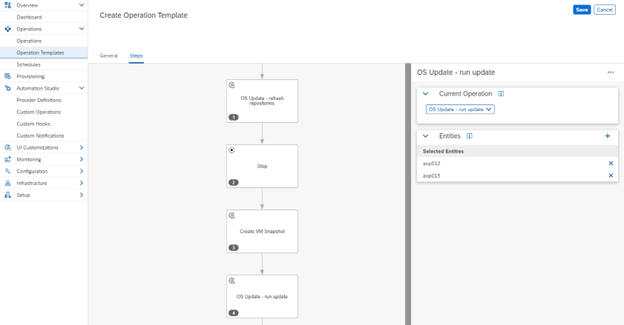
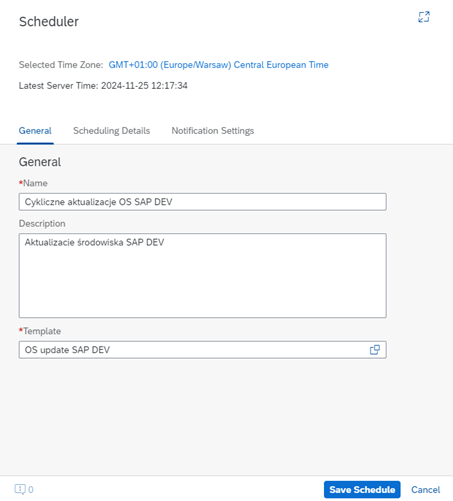
However, this does not mean that the use of LaMa in the Standard version is limited solely to managing the startup and shutdown of systems. It also enables the creation of automated processes by configuring custom operations, which can be assigned to selected objects such as SAP systems, their instances, or virtual machines, through custom scripts and extensions that do not violate SAP licenses.
Such an approach allows organizations using the Standard version to enhance the functionality of the tool in a way that is tailored to their needs, while maintaining compliance with licensing policies.